二手车交易价格预测
一、赛题与数据
1.赛题数据
赛题以预测二手车的交易价格为任务,数据集报名后可见并可下载,该数据来自某交易平台的二手车交易记录,总数据量超过40w,包含31列变量信息,其中15列为匿名变量。为了保证比赛的公平性,将会从中抽取15万条作为训练集,5万条作为测试集A,5万条作为测试集B,同时会对name、model、brand和regionCode等信息进行脱敏。
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| SaleID | 交易ID,唯一编码 |
| name | 汽车交易名称,已脱敏 |
| regDate | 汽车注册日期,例如20160101,2016年01月01日 |
| model | 车型编码,已脱敏 |
| brand | 汽车品牌,已脱敏 |
| bodyType | 车身类型:豪华轿车:0,微型车:1,厢型车:2,大巴车:3,敞篷车:4,双门汽车:5,商务车:6,搅拌车:7 |
| fuelType | 燃油类型:汽油:0,柴油:1,液化石油气:2,天然气:3,混合动力:4,其他:5,电动:6 |
| gearbox | 变速箱:手动:0,自动:1 |
| power | 发动机功率:范围 [ 0, 600 ] |
| kilometer | 汽车已行驶公里,单位万km |
| notRepairedDamage | 汽车有尚未修复的损坏:是:0,否:1 |
| regionCode | 地区编码,已脱敏 |
| seller | 销售方:个体:0,非个体:1 |
| offerType | 报价类型:提供:0,请求:1 |
| creatDate | 汽车上线时间,即开始售卖时间 |
| price | 二手车交易价格(预测目标) |
| v系列特征 | 匿名特征,包含v0-14在内15个匿名特征 |
2.评测指标
本赛题的评价标准为MAE(Mean Absolute Error)

分类算法常见的评估指标如下:
- 对于二类分类器/分类算法,评价指标主要有accuracy, [Precision,Recall,F-score,Pr曲线],ROC-AUC曲线。
- 对于多类分类器/分类算法,评价指标主要有accuracy, [宏平均和微平均,F-score]。
对于回归预测类常见的评估指标如下:
- 平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Error,MAE),均方误差(Mean Squared Error,MSE),平均绝对百分误差(Mean Absolute Percentage Error,MAPE),均方根误差(Root Mean Squared Error), R2(R-Square)
3.结果提交格式
提交前请确保预测结果的格式与sample_submit.csv中的格式一致,以及提交文件后缀名为csv。
SaleID,price
150000,687
150001,1250
150002,2580
150003,1178
二、赛题理解
1.分析赛题
-
此题为传统的数据挖掘问题,通过数据科学以及机器学习深度学习的办法来进行建模得到结果。
-
此题是一个典型的回归问题。
-
主要应用xgb、lgb、catboost,以及pandas、numpy、matplotlib、seabon、sklearn、keras等等数据挖掘常用库或者框架来进行数据挖掘任务。
-
通过EDA来挖掘数据的联系和自我熟悉数据。
2.经验总结
作为切入一道赛题的基础,赛题理解是极其重要的,对于赛题的理解甚至会影响后续的特征工程构建以及模型的选择,最主要是会影响后续发展工作的方向,比如挖掘特征的方向或者存在问题解决问题的方向,对了赛题背后的思想以及赛题业务逻辑的清晰,也很有利于花费更少时间构建更为有效的特征模型,赛题理解要达到的地步是什么呢,把一道赛题转化为一种宏观理解的解决思路。 以下将从多方面对于此进行说明:
- 1) 赛题理解究竟是理解什么: 理解赛题是不是把一道赛题的背景介绍读一遍就OK了呢?并不是的,理解赛题其实也是从直观上梳理问题,分析问题是否可行的方法,有多少可行度,赛题做的价值大不大,理清一道赛题要从背后的赛题背景引发的赛题任务理解其中的任务逻辑,可能对于赛题有意义的外在数据有哪些,并对于赛题数据有一个初步了解,知道现在和任务的相关数据有哪些,其中数据之间的关联逻辑是什么样的。 对于不同的问题,在处理方式上的差异是很大的。如果用简短的话来说,并且在比赛的角度或者做工程的角度,就是该赛题符合的问题是什么问题,大概要去用哪些指标,哪些指标是否会做到线上线下的一致性,是否有效的利于我们进一步的探索更高线上分数的线下验证方法,在业务上,你是否对很多原始特征有很深刻的了解,并且可以通过EDA来寻求他们直接的关系,最后构造出满意的特征。
- 2) 有了赛题理解后能做什么: 在对于赛题有了一定的了解后,分析清楚了问题的类型性质和对于数据理解的这一基础上,是不是赛题理解就做完了呢? 并不是的,就像摸清了敌情后,我们至少就要有一些相应的理解分析,比如这题的难点可能在哪里,关键点可能在哪里,哪些地方可以挖掘更好的特征,用什么样得线下验证方式更为稳定,出现了过拟合或者其他问题,估摸可以用什么方法去解决这些问题,哪些数据是可靠的,哪些数据是需要精密的处理的,哪部分数据应该是关键数据(背景的业务逻辑下,比如CTR的题,一个寻常顾客大体会有怎么样的购买行为逻辑规律,或者风电那种题,如果机组比较邻近,相关一些风速,转速特征是否会很近似)。这时是在一个宏观的大体下分析的,有助于摸清整个题的思路脉络,以及后续的分析方向。
- 3) 赛题理解的-评价指标: 为什么要把这部分单独拿出来呢,因为这部分会涉及后续模型预测中两个很重要的问题: 1. 本地模型的验证方式,很多情况下,线上验证是有一定的时间和次数限制的,所以在比赛中构建一个合理的本地的验证集和验证的评价指标是很关键的步骤,能有效的节省很多时间。 2. 不同的指标对于同样的预测结果是具有误差敏感的差异性的,比如AUC,logloss, MAE,RSME,或者一些特定的评价函数。是会有很大可能会影响后续一些预测的侧重点。
- 4) 赛题背景中可能潜在隐藏的条件: 其实赛题中有些说明是很有利益-都可以在后续答辩中以及问题思考中所体现出来的,比如高效性要求,比如对于数据异常的识别处理,比如工序流程的差异性,比如模型运行的时间,比模型的鲁棒性,有些的意识是可以贯穿问题思考,特征,模型以及后续处理的,也有些会对于特征构建或者选择模型上有很大益处,反过来如果在模型预测效果不好,其实有时也要反过来思考,是不是赛题背景有没有哪方面理解不清晰或者什么其中的问题没考虑到。
3.指标的补充解释

true positive: correctly identified as positive(预测为真,预测正确,真实为真)
false positive: wrongly identified as positive(预测为真,预测错误,真实为假)
false negative: (预测为假,预测错误,真实为真)
true negative: (预测为假,预测真确,真实为假)
-
Precision:how many selected items are relevant ?
-
Precision is a measure that tells us what proportion of patients that we diagnosed as having cancer, actually had cancer.
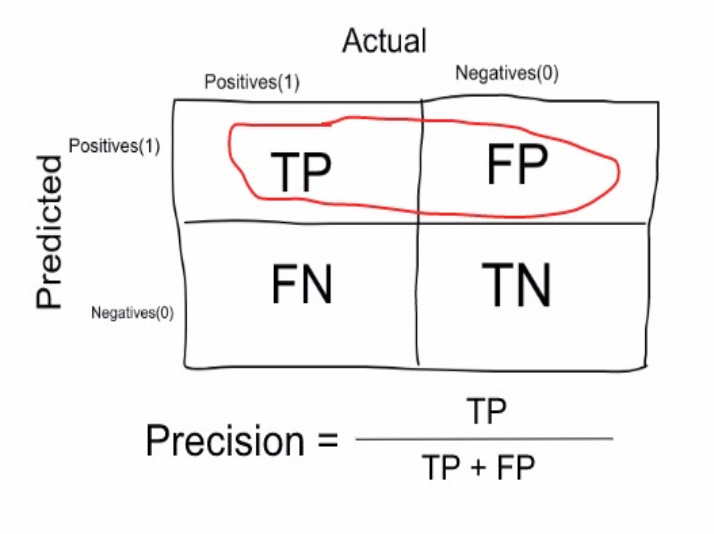
-
-
Recall or Sensitivity:how many relevant items are selected ?
-
Recall is a measure that tells us what proportion of patients that actually had cancer was diagnosed by the algorithm as having cancer.
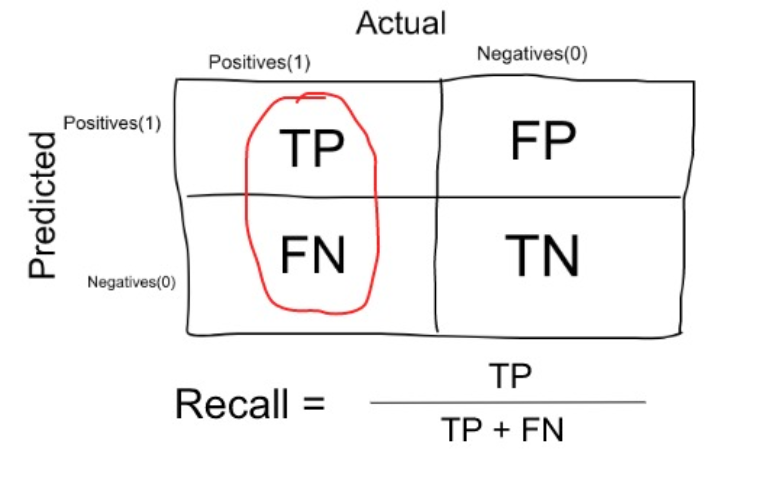
-
When to use Precision and When to use Recall?:
It is clear that recall gives us information about a classifier’s performance with respect to false negatives (how many did we miss), while precision gives us information about its performance with respect to false positives (how many did we caught).
-
Precision is about being precise . So even if we managed to capture only one cancer case, and we captured it correctly, then we are 100% precise.
-
Recall is not so much about capturing cases correctly but more about capturing all cases that have “cancer” with the answer as “cancer”. So if we simply always say every case as “cancer”, we have 100% recall.
-
-
Accuracy
- Accuracy in classification problems is the number of correct predictions made by the model over all kinds predictions made.
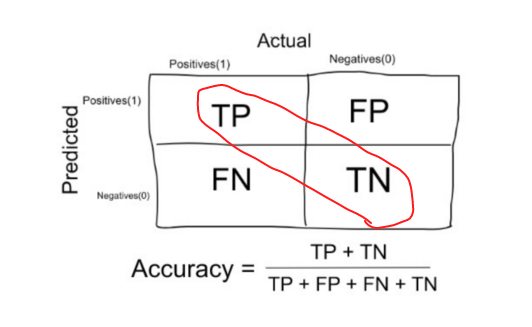
-
When to use Accuracy:
Accuracy is a good measure when the target variable classes in the data are nearly balanced.
Ex:60% classes in our fruits images data are apple and 40% are oranges.
-
When NOT to use Accuracy:
Accuracy should NEVER be used as a measure when the target variable classes in the data are a majority of one class.
Ex: In our cancer detection example with 100 people, only 5 people has cancer.
-
AUC - ROC Curve
-
AUC - ROC curve is a performance measurement for classification problem at various thresholds settings. ROC is a probability curve and AUC represents degree or measure of separability. It tells how much model is capable of distinguishing between classes.

👍Case1: When two curves don’t overlap at all means model has an ideal measure of separability. It is perfectly able to distinguish between positive class and negative class.
🤔Case2: When AUC is 0.7, it means there is 70% chance that model will be able to distinguish between positive class and negative class.
❌Case3: This is the worst situation. When AUC is approximately 0.5, model has no discrimination capacity to distinguish between positive class and negative class.
Case4: When AUC is approximately 0, model is actually reciprocating the classes. It means, model is predicting negative class as a positive class and vice versa.
AUC ROC 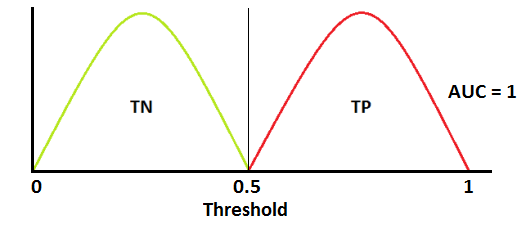







-